Encryption and Decryption
Kānuka uses open standards for encryption, and all the code is open source. For the symmetric key, Kānuka uses the AES 256-bit standard. For the public/private key pair, Kānuka uses the RSA 2048-bit standard. Both these standards are used widely across the internet. RSA is used any time you browse the internet with an HTTPS connection, while AES is used whenever you are logged into the Wi-Fi router.
Why RSA?
Section titled “Why RSA?”Kānuka uses RSA keys exclusively for asymmetric encryption. While modern alternatives like Ed25519 exist, RSA was chosen for several reasons:
-
Direct encryption support — RSA can directly encrypt data, which is exactly what Kānuka needs to encrypt symmetric keys. Ed25519 is a signature-only algorithm and cannot encrypt data directly. Using it for encryption would require implementing additional cryptographic schemes, adding complexity and potential for errors.
-
Universal tooling — RSA keys can be generated with any SSH or OpenSSL tool (
ssh-keygen -t rsa,openssl genrsa). While Ed25519 support is growing, RSA remains the most universally compatible option. -
Sufficient security — RSA-2048 provides approximately 112 bits of security, which is more than sufficient for Kānuka’s use case. The performance advantages of Ed25519 are irrelevant when encrypting small symmetric keys infrequently.
-
Simplicity — Supporting a single key type keeps the codebase simple, reduces testing burden, and eliminates user confusion about which key type to use.
How does Kānuka work?
Section titled “How does Kānuka work?”Here is the basic workflow for encryption, assuming you have access:
- Kānuka will search your entire repo for every file that has
.envin the name, but not.kanuka. - Kānuka will then use your private key to decrypt your symmetric key that
resides in
project_root/.kanuka/secrets/your_username.kanuka. - Kānuka will use that decrypted symmetric key to encrypt every file found in step 1.
- Kānuka will then name those files exactly the same, just with
.kanukaadded onto the end.
For decryption, the same is done just in reverse. Instead of searching for all
.env files, it will search for all .kanuka files.
Why is this secure?
Section titled “Why is this secure?”Kānuka is secure because all sensitive information is only ever in memory or on your local device.
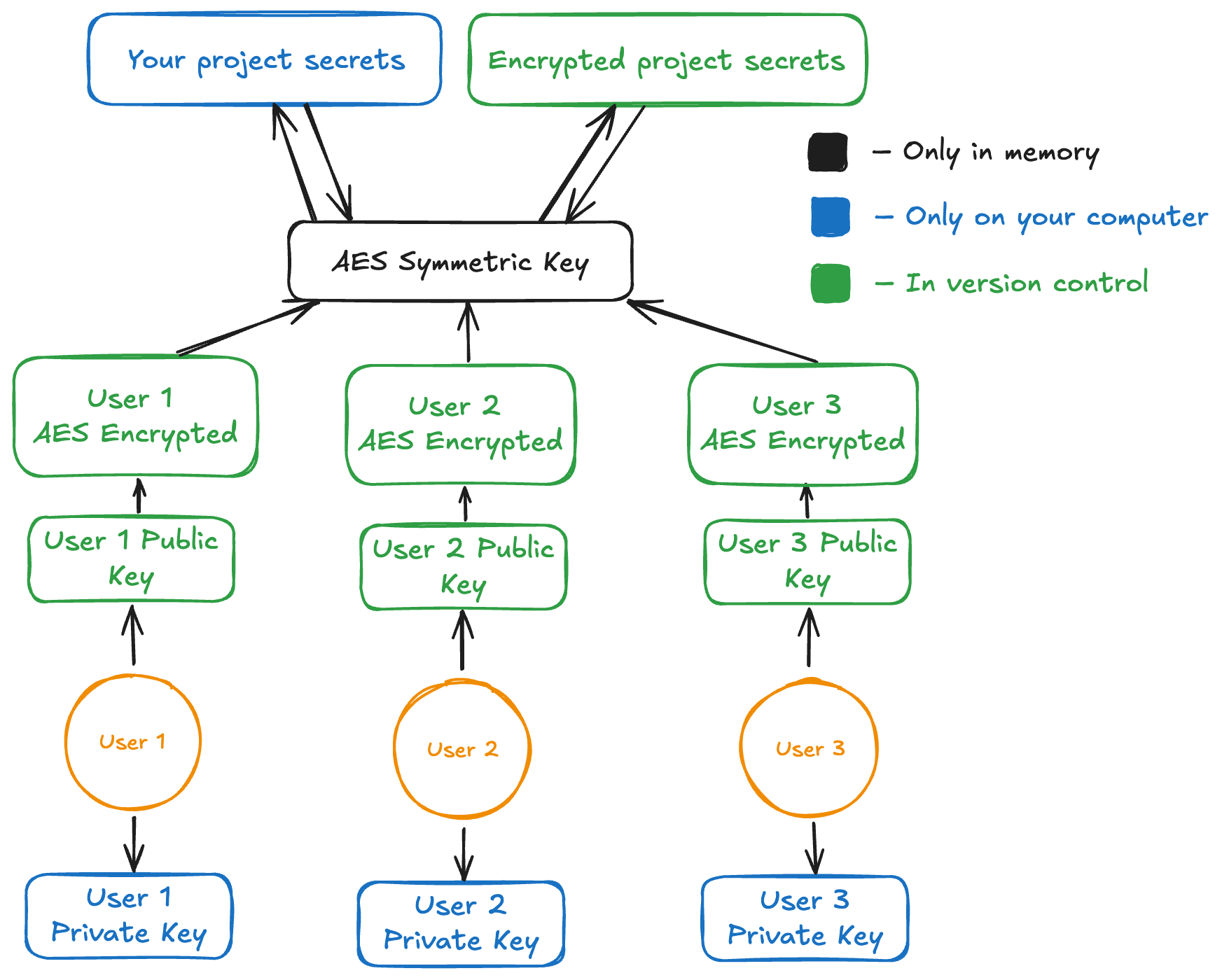
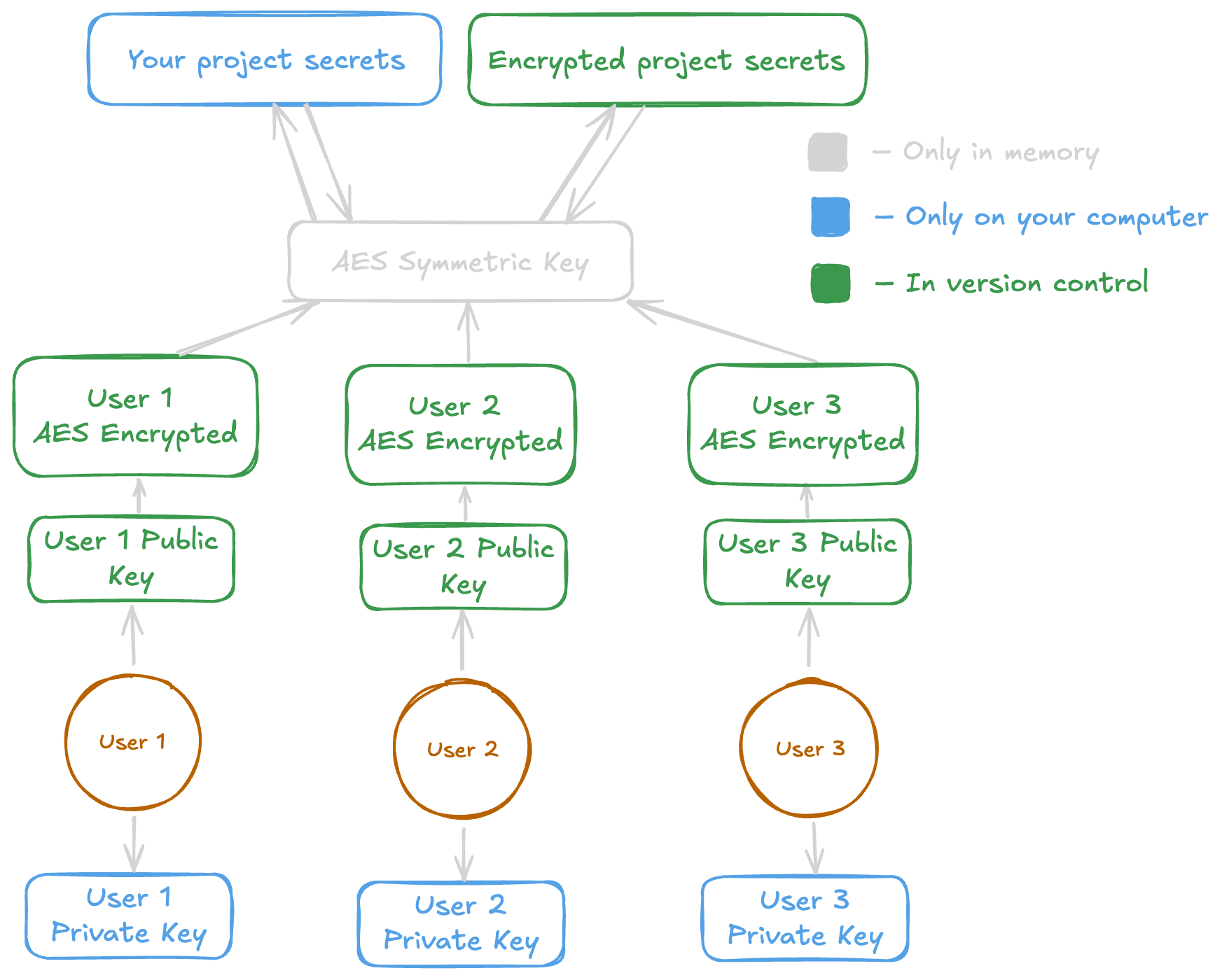
These are — in broad strokes — what ends up happening during an encryption and decryption process.
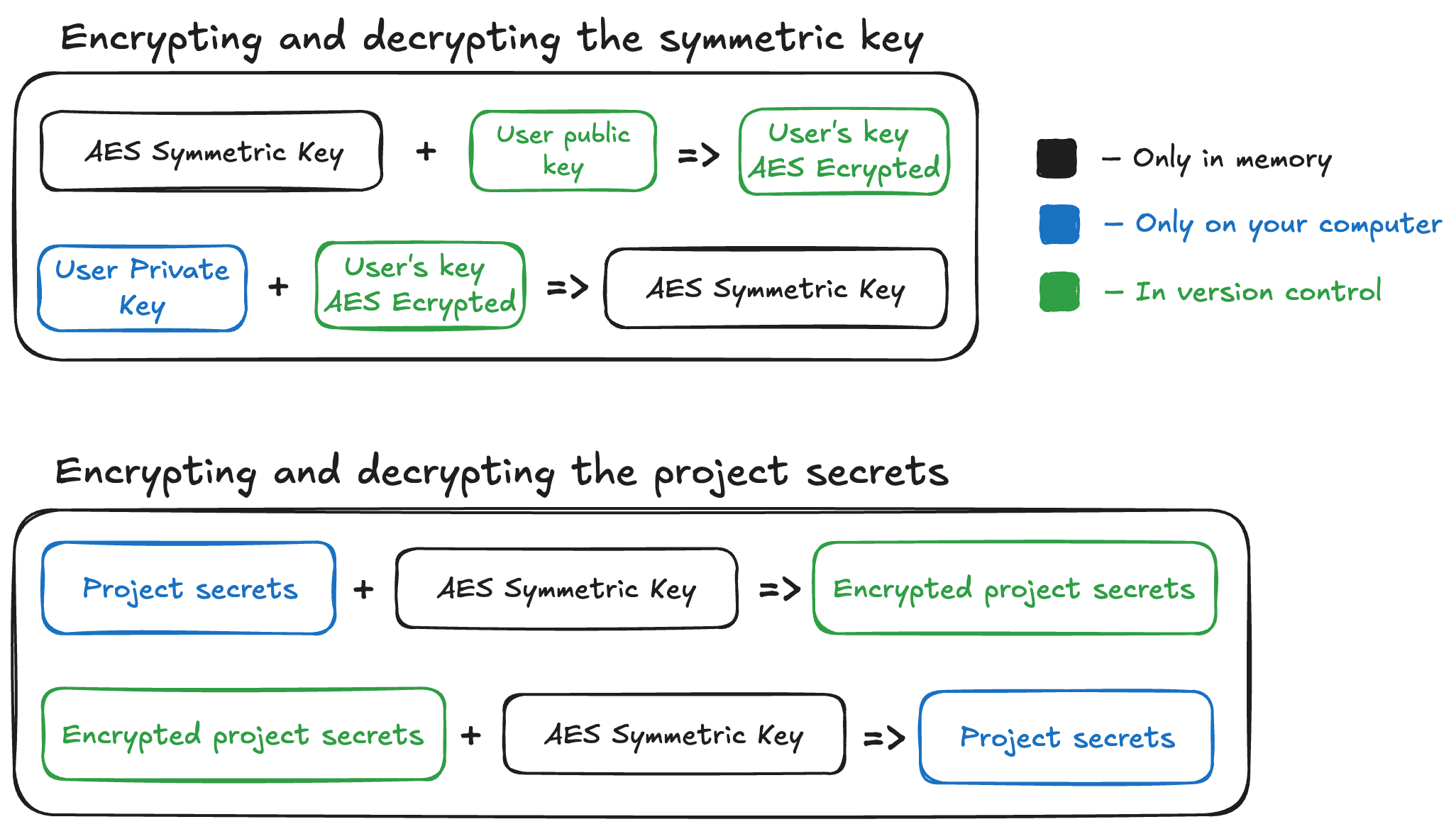
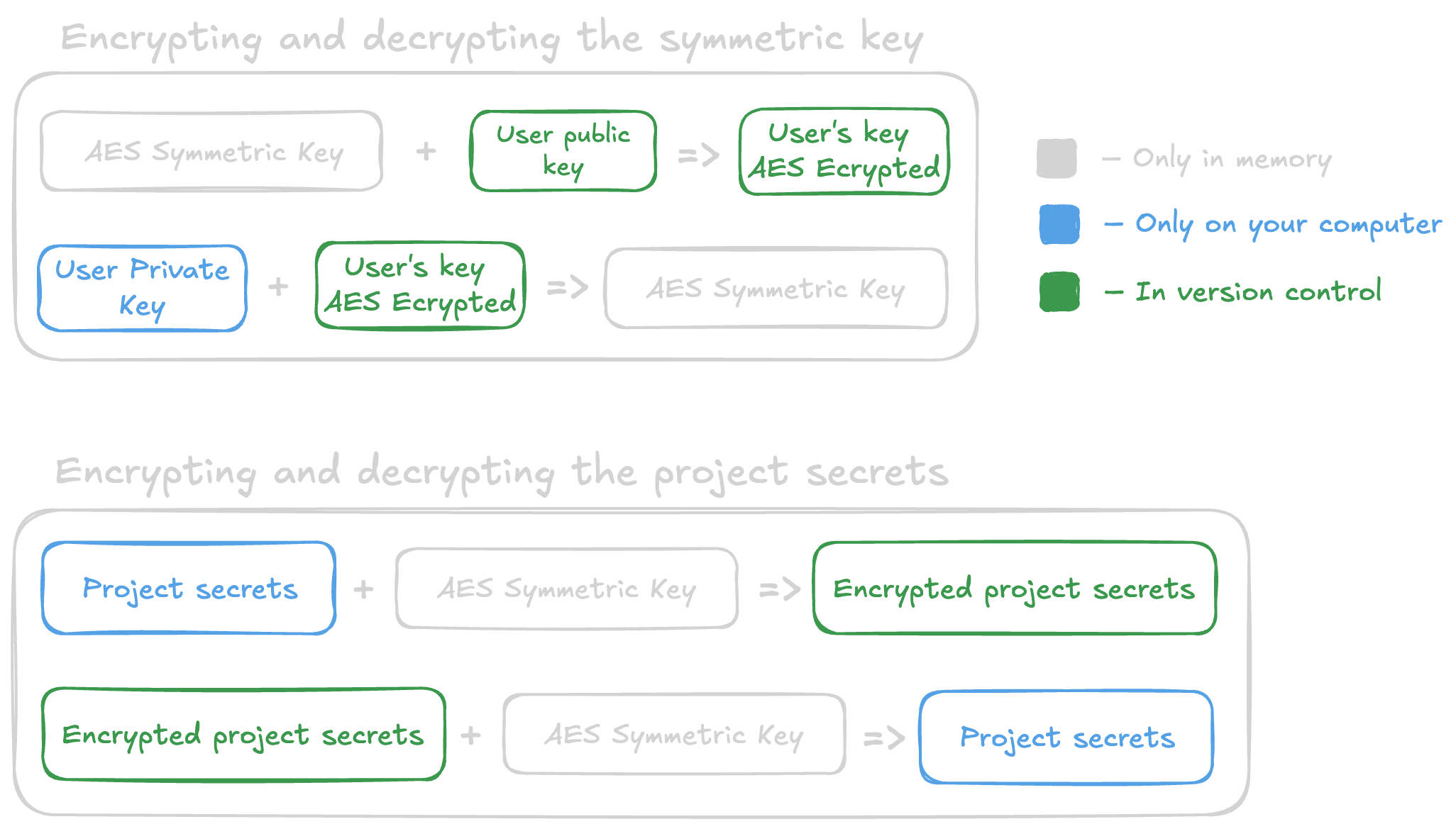
Continue reading to learn about what happens during registration.